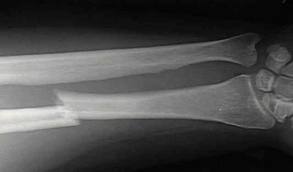
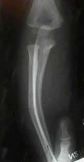
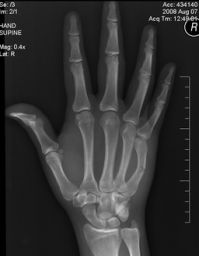
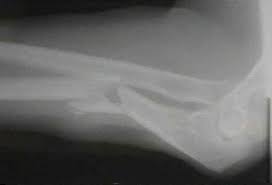
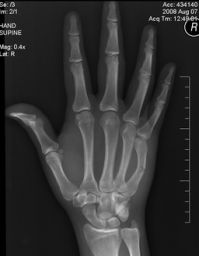
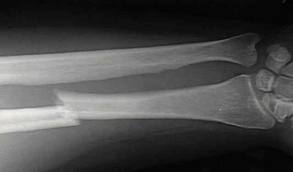
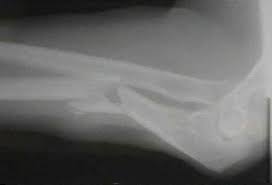
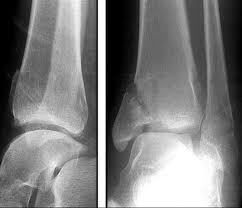
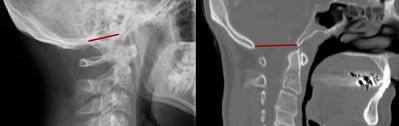
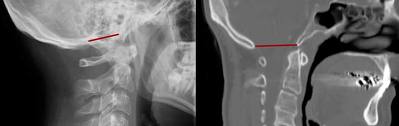
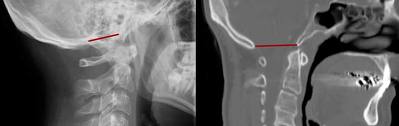
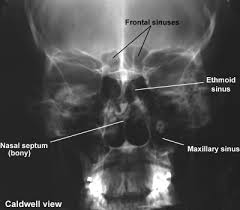
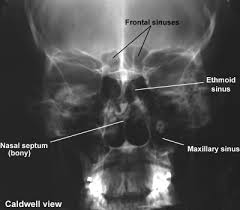
8.
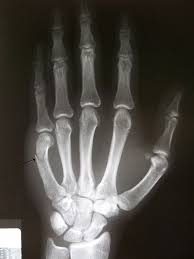
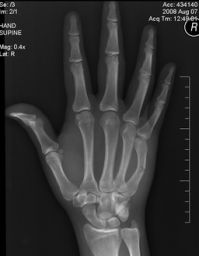
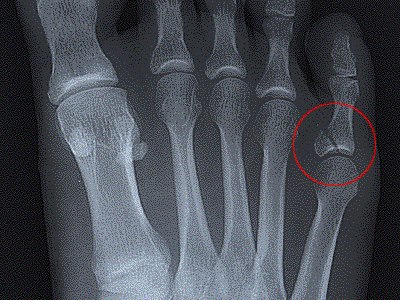
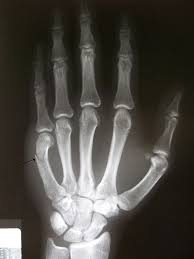
Also known as radiographic noise, this refers to the random nature in which x-rays interact with the image receptor. If x-rays are produced with just a few photons, the radiographic noise will be higher. A granular or spotty, non-uniformity of the x-ray image results. The use of high MAS, low KVP, and slower image receptors reduce radiographic noise.