Atomic number (Z)
Metalic crystals
Protons
Atomic nucleus
Niels Bohr
Chemical bond
Covalent crystals
Metalic bond
Jonh Dalton
J. J. Thomson
Atomic Shell
Periodic Table of Elements
Molecule
Isotopes
Ernest Rutherford
Ionic bond
Ions
Mass number (A)
Neutrons
Atom
Molecule properties
Electrons
Ionic crystals
Covalent bond
Heavy uncharged particles found within atomic nuclei
The sum of the number of neutrons and protons in an atomic nucleus
A chemical bond formed when non-metal atoms share electrons

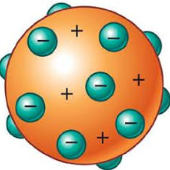
Charged atoms
A grouping of electrons surrounding the nucleus of an atom
An attraction between a positive metal ion and the electrons surrounding it
The smallest unit of matter that constitutes a chemical element.
Heavy positively charged particles found within atomic nuclei.
From low to high melting and boiling points, insoluble in water and very good electrical conductors
A table that classifies elements by their physical and chemical properties; rows are called periods; columns are called groups;
Liquids or gases at room temperature. Some can be solid, but they melt at low temperatures.
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
An atom's dense central core, containing protons and neutrons.
Very high melting and boiling points, insoluble in water and not good electrical conductors

Formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one metal to non-metal atom
Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons
Negatively charged particles, with very small mass, found outside the nucleus
The force that holds atoms together
Two or more non-metal atoms held together by covalent bonds

Very high melting and boiling points, soluble in water and good electrical conductors in solution or molten